Theoretical calculations of the kinetics of the OH reaction with 2-methyl-2-propen-1-ol and its alkene analogue†
Abstract
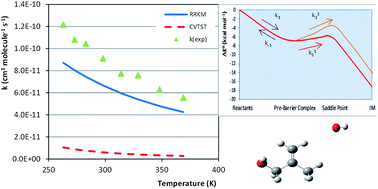
In this work, the first and rate determining steps of the mechanism of the OH addition to 2-methyl-2-propen-1-ol (MPO221) and methylpropene (M2) have been studied at the DFT level, employing the BH and HLYP functional and the cc-pVDZ and aug-cc-pVDZ basis sets. The thermochemical properties of equilibrium (enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energies) have been determined within the conventional statistical thermodynamics relations and the rate coefficients have been determined on the basis of the variational transition state theory. The adoption of the microcanonical variational transition state theory was proved to be crucial for the description of the kinetics of OH addition to these unsaturated compounds. The rate coefficients obtained for the OH reactions with MPO221 and M2 at 298.15 K deviate, respectively, 27% and 13% from the experimental rate coefficient available in the literature. A non-Arrhenius profile is observed for the rate coefficients. Moreover, the values of the rate coefficients for the MPO221 + OH reaction are greater than those for the M2 + OH reaction, suggesting that the substitution of the hydrogen atom in an alkene by the –OH functional group increases the reactivity with respect to the hydroxyl radical.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...