Synthesis of zinc–nickel ferrite nanorods and their magnetic properties
Abstract
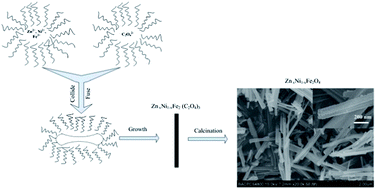
Zinc–nickel (Zn–Ni) ferrite nanorods were synthesized by a microemulsion-based method in combination with calcination at different temperatures. The morphologies and structures of Zn–Ni ferrite nanorods and their precursors of Zn–Ni–Fe composite oxalate nanorods were characterized using field emission scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Magnetization measurements were carried out using a vibrating sample magnetometer at room temperature. It was shown that the Zn–Ni ferrite nanorods were around 50–200 nm in diameter and several micrometers in length. Their saturation magnetization increased with increasing calcination temperature from 350 to 900 °C. In addition, the magnetic properties of the Zn–Ni ferrite nanorods were also affected by their composition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...