Crystal structure, topology, tiling and photoluminescence properties of 4d–4f hetero-metal organic frameworks based on 3,5-pyrazoledicaboxylate†
Abstract
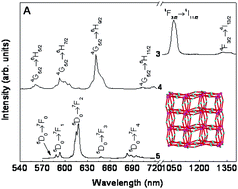
Reaction of lanthanide oxides, cadmium acetate and 3,5-pyrazoledicarboxylic acid under hydrothermal conditions afforded five new isostructural 4d–4f hetero-metal organic frameworks, [Cd3Ln(pdc)3(H2O)] {H3pdc = 3,5-pyrazoledicarboxylic acid, Ln = La (1), Pr (2), Nd (3), Sm (4) and Eu (5)}. All compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The compounds feature a very interesting 3D structure built up from a secondary building unit, [Cd12Ln8(pdc)6], and possess a new topology type and complicated unique tiling. The solid state photoluminescence properties of compounds 3–5 were investigated at room temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...