Predicted stability, structures, and magnetism of 3d transition metal nitrides: the M4N phases†
Abstract
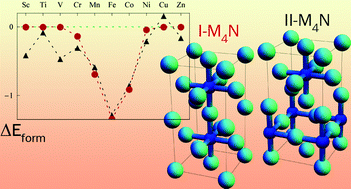
The 3d transition metal nitrides M4N (Sc4N, Ti4N, V4N, Cr4N, Mn4N, Fe4N, Co4N, Ni4N, and Cu4N) have unique phase relationships, crystal structures, and electronic and magnetic properties. Here we present a systematic density functional theory (DFT) study on these transition metal nitrides, assessing both the I-M4N phase and the II-M4N phase, which differ in ordering of the N atoms within the face-centered cubic (FCC) framework of metal atoms. The calculations showed that for M = Mn, Fe, Co and Cu, the I-M4N phases with perfect metal sub-lattices are favored, while for M = Sc–Cr, and Ni, the II-M4N phases with distorted metal sub-lattices are favored. We predict that several currently not existing II-M4N phases may be synthesized experimentally as metastable phases. From Bader charge analysis the M4N phases are found to be ionic with significant metal–metal bonding. I-M4N with M = Cr to Ni are magnetic, while II-M4N with M = Cr and Ni are non-magnetic. The calculations revealed unusually high local magnetic moments and high spin-polarization ratios of the M1 atoms in I-M4N (M = Cr to Ni). The origin of magnetism and lattice distortion of the M4N phases is addressed with the Stoner criterion. Detailed information about the relative stability, structures, chemical bonding, as well as the electronic and magnetic properties of the phases are of interest to a wide variety of fields, such as chemical synthesis, catalysis, spintronics, coating technology, and steel manufacturing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...