A novel photosensitized Fenton reaction catalyzed by sandwiched iron in synthetic nontronite†
Abstract
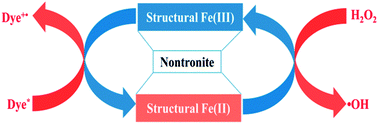
The conventional photo-Fenton reaction often suffers from the constraints of operation pH, low iron loading, ultraviolet availability in solar light and instability of iron-based catalysts. Here we report a novel heterogeneous Fenton reaction which works with a dye-photosensitized structural Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox cycling mechanism. The synthesized nontronite catalyst (NAU) was characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and thermal gravimetric analysis (TG). NAU exhibited excellent catalytic activity over a wide pH range (3.0–8.0) for highly efficient degradation of Rhodamine B by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) under visible light irradiation (λ > 420 nm). The excited dye molecule donates electrons to structural iron sandwiched in NAU which further catalyzes H2O2 to generate highly reactive ˙OH radicals. This iron-rich clay mineral (total Fe, 24.4 wt%) is chemically and mechanically stable. There are no measurable iron leaching, nor any noticeable loss of activity and damage to the clay structure observed after 6 recycles. Therefore, NAU clay has outstanding merits for the practical treatment of organic dye pollutants at large scale.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...