Solar light driven Rhodamine B degradation over highly active β-SiC–TiO2 nanocomposite†
Abstract
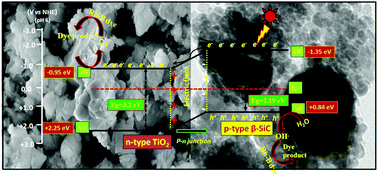
A series of β-SiC–TiO2 nanocomposites were successfully fabricated by a sol–gel process with the purpose of efficient charge (e−, h+) separation and the enhancement of the photocatalytic performance under solar light irradiation. A pristine anatase state of TiO2 was prepared by the acid hydrolysis of Ti (OiPr)4 and a β-SiC powder was synthesized by a thermal plasma process from rice husks. The physicochemical characteristics of the nanocomposites were surveyed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-visible diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS), BET surface area, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and photoelectrochemical (PEC) measurement. The PEC study confirms that TiO2 is n-type semiconductor, whereas the β-SiC is p-type semiconductor. The XRD, TEM and XPS studies confirm the formation of a heterojunction between the β-SiC and TiO2. The photocatalytic activities of all the β-SiC–TiO2 nanocomposites were studied for aqueous Rhodamine B (Rh-B) dye degradation under solar light irradiation. The photodegradation mechanism of all the synthesized catalysts were further confirmed through chemical oxygen demand (COD) analysis and trapping of hydroxyl radicals by a fluorescence probe technique. Among all the samples, 20 wt% β-SiC–TiO2 exhibits a significant activity of 87% dye degradation in the presence of solar light. The high activity of 20 wt% β-SiC–TiO2 is ascribed to high surface area, low crystallite size, high generation of OH radicals and COD efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...