Dual functional ionic liquids as antimicrobials and plasticisers for medical grade PVCs†
Abstract
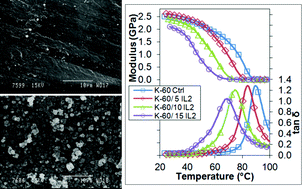
Two ionic liquids, 1-ethylpyridinium docusate (IL1) and tri-n-butyl(2-hydroxyethyl)phosphonium docusate (IL2), were designed and synthesized with the explicit intention of imparting a combination of plasticization and antimicrobial efficacy when incorporated into medical grade poly(vinyl chloride)s (PVCs). The glass transition (Tg) of PVC can be reduced by >20 °C on addition of 15 wt% IL2. Both IL1 and IL2 leached to varying extents from the base PVC resins rendering the surface of the PVCs hydrophilic. The antimicrobial activity of both ILs is related to the presence and concentration of both cationic and anionic component of the ILs leached from the PVC and inversely proportional to the extent of PVC gelation. Blends of the PVCs with IL1 displayed antibacterial activity against almost all Gram-positive bacteria tested, including coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CoNS) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), but not with IL2 at low concentration in contrast to our previous study when high concentrations of IL2 were used. The more hydrophilic IL1 when added to PVC retards biofilm formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...