New clicked thiirane derivatives as gelatinase inhibitors: the relevance of the P1′ segment†
Abstract
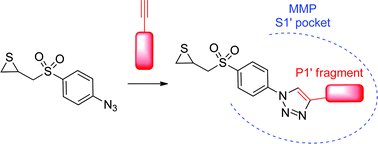
Gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9), a subfamily of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs), are involved in several pathologies and especially in cancer. Thiirane is a latent-zinc binding group used for the design of potent inhibitors of gelatinases. Here we report a new family of thiirane inhibitors, obtained by click chemistry. Thus, an azide fragment containing the thiirane group was connected to several lipophilic alkynes, which were designed to interact with the S1′ pocket of the two gelatinases. Our hit compound (2f) displayed submicromolar inhibition of MMP-2 (IC50 = 0.62 μM). Computational studies have been used to compare the binding mode of compound 2f in MMP-2 with the reference thiirane inhibitor (SB-3CT), allowing us to discuss the relevance of the P1′ segment in order to maximize potency.
- This article is part of the themed collection: A Decade of Progress in Click Reactions Based on CuAAC

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...