Silymarin coated gold nanoparticles ameliorates CCl4-induced hepatic injury and cirrhosis through down regulation of hepatic stellate cells and attenuation of Kupffer cells†
Abstract
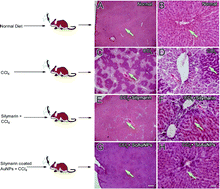
Silymarin coated gold nanoparticles with a mean size of 20 nm were synthesized and functionalized in one pot using silymarin as a reducing and stabilizing agent. Conjugation of gold with silymarin was confirmed with FT-IR and UV-visible techniques. The aim of this study was to investigate the hepatoprotective and antifibrotic potential of Silymarin coated gold nanoparticles. For this purpose oxidative liver damage was induced in Wistar rats by intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 dissolved in olive oil (1 : 1 v/v, 1 ml kg−1). Silymarin coated gold nanoparticles were administered intragastrically once per day for 14 weeks in a dose of 30 mg kg−1 of body weight. Hepatoprotective and antifibrotic activities of silymarin coated gold nanoparticles were assessed in terms of reduction in serum enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP), through histopathology and immunohistochemistry techniques. It also reduced the CCl4-induced damaged area as well as fibrotic area to 0% as assessed by histopathology. The Alpha SMA and Kupffer cells were also reduced in number around the portal traid area by the silymarin coated gold nanoparticles. These hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects were better than the positive control silymarin. Our results suggest the therapeutic effect of silymarin coated gold nanoparticles in CCl4-induced liver injury and cirrhosis by promoting extracellular matrix degradation, hepatic stellate cells inactivation with strong enhancement of hepatic regenerative capacity. Silymarin coated gold nanoparticles could be administered for up to 14 weeks without inducing side effects or alterations of the histological structure of kidneys, heart, pancreas and lungs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...