Enhanced thermochemical CO2 splitting over Mg- and Ca-doped ceria/zirconia solid solutions
Abstract
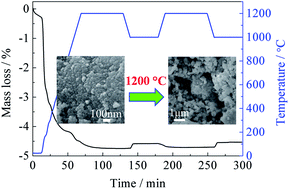
Thermochemical CO2 splitting was carried out over ceria/zirconia solid solutions prepared via a P123-added hydrothermal method in the temperature range of 1100–1400 °C. XRD, Raman and TPR characterization indicated that the introduction of Mg and Ca into ceria/zirconia could produce lattice defects in the fluorite lattice, and then strongly modify the mobility of oxygen as well as the thermal stability of the samples. As compared to Mg-doped samples, faster reaction rates and higher CO2 splitting reactivity were obtained over Ca-doped samples, because of the faster oxygen mobility in Ca–Ce–Zr–O ternary solid solutions. Moreover, the porous structure with small particle size favoured the thermal reduction and the mass diffusion. As a result, fast reaction rates and relatively high fuel productivity were obtained at the moderate thermal reduction temperature (1200 °C).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...