Dependence of the electron transfer capacity on the kinetics of quinone-mediated Fe(iii) reduction by two iron/humic reducing bacteria†
Abstract
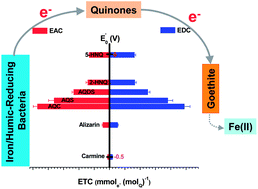
The effects of a series of quinones on goethite reduction by two types of iron/humic reducing bacteria (Shewanella decolorationis S12 and Aeromonas hydrophila HS01) were investigated in this study. The results showed that the quinones with redox potentials (Eh0) in the range of −344 to −137 mV (vs. SHE at pH 7) can significantly accelerate Fe(III) reduction by S12 and HS01. Plots of the electron transfer capacities (ETC) of the quinones (including the electron accepting and donating capacities determined using chronoamperometry) vs. Eh0 were similar to those of the ratios of iron reduction rates with quinones to those without quinones (kcell+Q/kcell) vs. Eh0. The UV/vis diffuse-transmittance absorption spectra of S12 and HS01 suggested the presence of outer membrane c-type cytochromes, which are responsible for the extracellular reduction of iron and quinones. The Eh0 of the different types of cytochromes varies within a broad potential window, which might influence the electron shuttling capacity of various quinones from microorganisms to iron. The kcell+Q/kcell of different quinones had a good linear relationship with their ETC, and the difference of the redox equilibria among the different quinones might correlate to their different performance of ETC and mediating microbial iron reduction. This work can help researchers understand the influence of redox properties of quinone compounds on microbial iron transformation in anoxic environments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...