Nitrogen- and oxygen-containing activated carbon nanotubes with improved capacitive properties†
Abstract
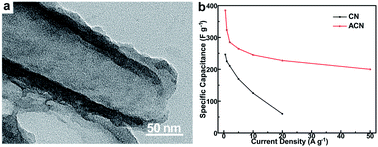
Nitrogen- and oxygen-containing activated carbon nanotubes have been successfully synthesized via a high temperature carbonization of polypyrrole (PPy) nanotubes followed by chemical activation. The first carbonization step ensures the formation of amorphous carbon nanotubes, which are more stable than PPy to preserve the nanotube morphology during the subsequent chemical activation process. The obtained activated carbon nanotubes with high nitrogen (19.8 wt%) and oxygen contents (11.1 wt%) show enlarged specific areas of 705.9 m2 g−1 compared to that of the pristine carbon nanotubes (212.4 m2 g−1). As expected, the activated carbon nanotubes exhibit enhanced capacitance properties, such as an enlarged specific capacity (384.9 F g−1 at 0.5 A g−1), excellent rate capability (201 F g−1 at 50 A g−1), and more stable cyclic stability (only 2.4% of specific capacitance loss after 500 cycles) due to its abundant micropores, high specific areas and abundant interfacial functional groups. This method is facile, low cost and enables easy production of large quantities, and can be expected to open up new opportunities in designing high-performance carbon electrode materials for supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...