Conversion of a zinc salicylate complex into porous carbons through a template carbonization process as a superior electrode material for supercapacitors†
Abstract
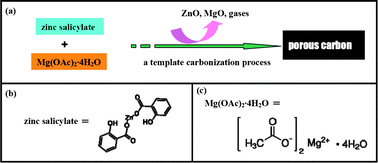
High performance porous carbons for supercapacitors have been successfully prepared through a template carbonization process with the help of magnesium acetate, using a zinc salicylate complex as a carbon source. The carbon–Zn–Mg-900 sample has amorphous features and a developed porous structure. Note that it has a high BET surface area of 2008 m2 g−1, a large pore volume of 3.44 cm3 g−1 and a rationally hierarchical pore size distribution. In a three-electrode system using 6 mol L−1 KOH as the electrolyte, it displays a high specific capacitance of 288.3 F g−1 at 1 A g−1, as well as a good rate capability and long term cycling durability (the retention is 96.6% after cycling 10 000 times). Furthermore, in a two-electrode system using [EMIm]BF4/AN as a mixed electrolyte, it reveals that operation temperatures of 25, 50, and 80 °C can greatly influence the electrochemical behavior. Higher operation temperatures can usually result in a better electrochemical performance. The measurements in a two-electrode system especially at different operation temperatures can, to a large extent, amplify the application scope of practical supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...