Magnetic molecularly imprinted microcapsules derived from Pickering emulsion polymerization and their novel adsorption characteristics for λ-cyhalothrin†
Abstract
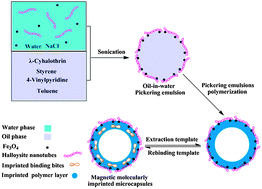
Magnetic molecularly imprinted microcapsules (MMIMs) were synthesized by Pickering emulsion polymerization. In this work, an oil-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) was first established in the presence of a few hydrophilic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetic separation carriers. The imprinting system was fabricated by radical polymerization and subsequent combination with functional and polymeric monomers in the oil phase. The formation mechanism of the Pickering emulsion and MMIMs is discussed in detail, and the as-prepared MMIMs are successfully evaluated as sorbents for the recognition of λ-cyhalothrin. The results demonstrated that the MMIMs exhibited magnetic sensitivity (Ms = 8.45 emu g−1), a hollow structure, a semipermeable external surface and excellent robustness. The batch mode experiments proved that the imprinting effect synchronously improved the adsorption kinetics and equilibrium for the MMIMs. The selective recognition experiments also suggested high affinity and selectivity of MMIMs towards λ-cyhalothrin over fenvalerate and diethyl phthalate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...