Nanostructured palladium-reduced graphene oxide platform for high sensitive, label free detection of a cancer biomarker†
Abstract
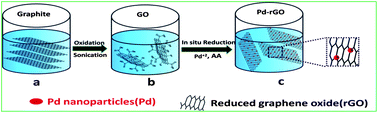
We report the results of studies related to the fabrication of a palladium nanoparticle decorated-reduced graphene oxide (Pd@rGO) based electrochemical immunosensor for the label free ultrasensitive detection of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a prostate cancer biomarker. The synergistic electrochemical activities of Pd and rGO result in an enhanced electron transfer used for the development of an ultrasensitive immunosensor. A facile approach was developed for the in situ synthesis of Pd@rGO using ascorbic acid as the reducing agent which enables the simultaneous reduction of both Pd+2 and GO into Pd nanoparticles and rGO, respectively. XRD, FTIR, SEM and TEM investigations were carried out to characterize the Pd@rGO material. A thin film of nanostructured Pd@rGO was electrophoretically deposited on an ITO coated glass electrode that was subsequently functionalized with anti-PSA antibodies. The electrochemical sensing results of the proposed immunosensor showed a high sensitivity {28.96 μA ml ng−1 cm−2}. The immunosensor is able to detect PSA at concentrations as low as 10 pg ml-1. The simple fabrication method, high sensitivity, good reproducibility and long term stability with acceptable accuracy in human serum samples are the main advantages of this immunosensor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...