Injectable enzymatically crosslinked hydrogels based on a poly(l-glutamic acid) graft copolymer†
Abstract
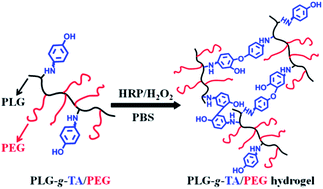
Enzymatically crosslinked injectable hydrogels based on poly(L-glutamic acid) grafted with tyramine and poly(ethylene glycol) (denoted as PLG-g-TA/PEG) were developed under physiological conditions in the presence of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Their gelation time, mechanical properties, swelling behaviors and porous structure were evaluated. The hydrogels were rapidly formed in the presence of low concentrations of HRP and H2O2. The storage modulus of the hydrogels could be well controlled and increased by increasing the concentrations of HRP and H2O2. The average pore-size of the hydrogels varied from 20 to 120 μm, depending on the H2O2 concentration. In addition, the encapsulated L929 fibroblast cells in the PLG-g-TA/PEG hydrogels exhibited high viability. After subcutaneous injection of the PLG-g-TA/PEG solutions containing HRP and H2O2 into the back of rats, the hydrogels were rapidly formed in situ. The hydrogels were found to persist for up to 10 weeks in vivo, and histological analysis indicated that the hydrogels exhibited acceptable biocompatibility. These results suggested that the biocompatible, injectable enzyme-mediated PLG-g-TA/PEG hydrogels are promising for biomedical applications including tissue engineering scaffolds and drug delivery carriers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...