pH-responsive layer-by-layer films of zwitterionic block copolymer micelles
Abstract
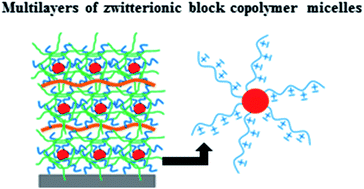
We report a strategy to incorporate micelles of poly[3-dimethyl (methacryloyloxyethyl) ammonium propane sulfonate]-block-poly[2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate] (βPDMA-b-PDPA) into electrostatic layer-by-layer (LbL) films. We obtained micelles with pH-responsive PDPA-cores and zwitterionic βPDMA-coronae at pH 8.5 through pH-induced self-assembly of βPDMA-b-PDPA in aqueous solution. To incorporate βPDMA-b-PDPA micelles into LbL films, we first obtained a net electrical charge on βPDMA-coronae. Negative charges of the zwitterionic units were screened through complexation of βPDMA-b-PDPA micelles and poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH). Positively charged micellar complexes were then self-assembled at the surface using poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) (PSS). The pH-stability of the multilayers was examined by exposing the films to decreasing pH values. Despite the disintegration of micellar complexes below pH 7, no change in film thickness was recorded between pH 8.5 and 3.5. Only ∼20% of the film released at pH < 3.5. Moreover, we demonstrated that when multilayers were exposed to decreasing pH at a temperature below the upper critical solution temperature (UCST) of betainized coronal chains, the film thickness increased by 20% between pH 4.5 and 3. This is probably due to phase separation of the corona block and formation of voids within the film, probably entrapping water molecules within the multilayers. Decreasing temperature also shifted the critical disintegration pH (onset of multilayer dissolution) to a slightly lower pH. By taking advantage of the pH-responsive cores, we showed that multilayers were capable of releasing functional molecules under moderately acidic conditions. Important biological properties of polybetaines, higher loading capacity of zwitterionic block copolymer micelles than linear polybetaines and pH-response of the multilayers at physiologically related pH values make such films promising for biomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...