Synthesis and characterization of diblock and statistical copolymers based on hydrolyzable siloxy silylester methacrylate monomers†
Abstract
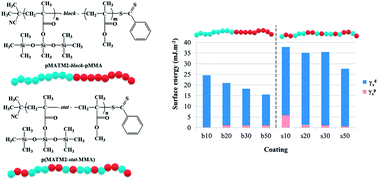
Statistical and diblock copolymers of bis(trimethylsiloxy)methylsilyl methacrylate (MATM2), a hydrolyzable monomer containing a silylester and a siloxane group, and methyl methacrylate (MMA) were synthesized by the RAFT process. The controlled character of the MATM2 RAFT polymerization using 2-cyanoprop-2-yl-dithiobenzoate (CPDB) or S-(2-cyanoprop-2-yl)-S-dodecyltrithiocarbonate as chain transfer agents was assessed by linear pseudo-first-order kinetics, linear molar mass growth with monomer conversion and low molar-mass dispersity. The hydrolysis kinetics of pMATM2 homopolymers was investigated by in situ1H-NMR and compared to several methacrylic homopolymers bearing hydrolyzable tri-alkylsilylester side groups. pMATM2-block-pMMA diblock copolymers were synthesized by in situ chain extension with methyl methacrylate, using pMATM2-CPDB as a macro-CTA. p(MATM2-stat-MMA) statistical copolymers were synthesized by simultaneous polymerization of MATM2 and MMA by the RAFT process. The monomer reactivity ratios for MATM2 (r1 = 1.29) and MMA (r2 = 0.62) were obtained from the Mayo Lewis equation using the least-squares method. All the copolymers synthesized by the RAFT process had molar masses close to the targeted values and low dispersities (ĐM < 1.15). DSC analysis and contact angle measurements revealed the influence of the copolymer microstructure (statistical or diblock) on their glass transition temperature and surface energy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...