Core cross-linked star (CCS) polymers with temperature and salt dual responsiveness: synthesis, formation of high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) and triggered demulsification†
Abstract
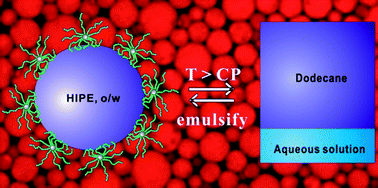
A series of five core cross-linked star (CCS) polymers has been synthesized by RAFT-mediated heterogeneous polymerization in aqueous media. These CCS polymers consist of poly(MEAx-co-PEGAy) (MEA is 2-methoxyethyl acrylate and PEGA is poly(ethylene glycol) acrylate) of different compositions. They exhibit responsiveness to both temperature and salt. Addition of kosmotropes reduces the cloud point, and addition of chaotropes raises the cloud point. These CCS polymers can stabilize dodecane-in-water high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) in the absence or presence of salts. Addition of salts has negligible effect on the maximum oil fraction, the size of oil droplets or the stability of the HIPEs. HIPEs with large oil fractions (up to 92 vol%) at low concentrations of CCS polymers (≤1 wt%) can be routinely obtained. When the oil volume fraction is larger than 74 vol%, gelled HIPEs are formed with long-term stabilities (more than three months). The temperature and salt responsiveness of the CCS polymers is transferred to the CCS-stabilized HIPEs. Addition of kosmotropes can enhance demulsification efficiency, while addition of chaotropes can decrease demulsification efficiency or enhance the thermal stability of the CCS-stabilized HIPEs. The emulsification–demulsification cycle can be successfully repeated four times. The facile and aqueous synthesis of CCS polymers and the fast response of the CCS-stabilized HIPEs will open up new opportunities for the preparation and exploitation of a range of smart soft materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...