Rh-catalyzed oxidative C–C bond formation and C–N bond cleavage: direct access to C2-olefinated free (NH)-indoles and pyrroles†
Abstract
The rhodium-catalyzed oxidative C2-olefination of indoles and pyrroles containing N-arylcarboxamide directing groups with a range of alkenes and subsequent cleavage of directing groups is described. This method provides direct and efficient access to C2-functionalized free (NH)-heterocycles.
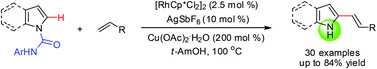

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...