Double-degradable responsive self-assembled multivalent arrays – temporary nanoscale recognition between dendrons and DNA†
Abstract
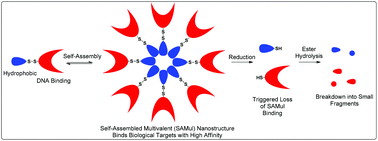
This article reports self-assembling dendrons which bind DNA in a multivalent manner. The molecular design directly impacts on self-assembly which subsequently controls the way these multivalent nanostructures bind DNA – this can be simulated by multiscale modelling. Incorporation of an S–S linkage between the multivalent hydrophilic dendron and the hydrophobic units responsible for self-assembly allows these structures to undergo triggered reductive cleavage, with dithiothreitol (DTT) inducing controlled breakdown, enabling the release of bound DNA. As such, the high-affinity self-assembled multivalent binding is temporary. Furthermore, because the multivalent dendrons are constructed from esters, a second slow degradation step causes further breakdown of these structures. This two-step double-degradation mechanism converts a large self-assembling unit with high affinity for DNA into small units with no measurable binding affinity – demonstrating the advantage of self-assembled multivalency (SAMul) in achieving highly responsive nanoscale binding of biological targets.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...