Synthesis and anti-toxoplasmosis activity of 4-arylquinoline-2-carboxylate derivatives†
Abstract
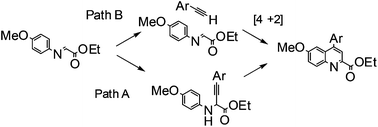
A one-step synthesis of 4-arylquinoline-2-carboxylates along with their antiprotozoal activity against the pathogenic parasite Toxoplasma gondii is reported. Mechanistic insights into the role of Lewis acid (silver triflate) versus Bronsted acid (triflic acid) catalysis are revealed clarifying aspects of the mechanism of the quinoline synthesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...