Supporting palladium metal on gold nanoparticles improves its catalysis for nitrite reduction†
Abstract
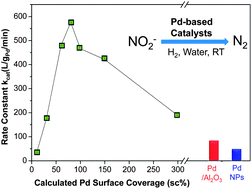
Nitrate (NO3−) and nitrite (NO2−) anions are often found in groundwater and surface water as contaminants globally, especially in agricultural areas due to nitrate-rich fertilizer use. One popular approach to studying the removal of nitrite/nitrate from water has been their degradation to dinitrogen via Pd-based reduction catalysis. However, little progress has been made towards understanding how the catalyst structure can improve activity. Focusing on the catalytic reduction of nitrite in this study, we report that Au NPs supporting Pd metal ("Pd-on-Au NPs") show catalytic activity that varies with volcano-shape dependence on Pd surface coverage. At room temperature, in CO2-buffered water, and under H2 headspace, the NPs were maximally active at a Pd surface coverage of 80%, with a first-order rate constant (kcat = 576 L gPd−1 min−1) that was 15x and 7.5x higher than monometallic Pd NPs (∼4 nm; 40 L gPd−1 min−1) and Pd/Al2O3 (1 wt% Pd; 76 L gPd−1 min−1), respectively. Accounting only for surface Pd atoms, these NPs (576 L gsurface-Pd−1 min−1) were 3.6x and 1.6x higher than monometallic Pd NPs (160 L gsurface-Pd−1 min−1) and Pd/Al2O3 (361 L gsurface-Pd−1 min−1). These NPs retained ∼98% of catalytic activity at a chloride concentration of 1 mM, whereas Pd/Al2O3 lost ∼50%. The Pd-on-Au nanostructure is a promising approach to improve the catalytic reduction process for nitrite and, with further development, also for nitrate anions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...