Observation of the origin of d0 magnetism in ZnO nanostructures using X-ray-based microscopic and spectroscopic techniques†
Abstract
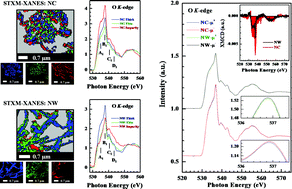
Efforts have been made to elucidate the origin of d0 magnetism in ZnO nanocactuses (NCs) and nanowires (NWs) using X-ray-based microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. The photoluminescence and O K-edge and Zn L3,2-edge X-ray-excited optical luminescence spectra showed that ZnO NCs contain more defects than NWs do and that in ZnO NCs, more defects are present at the O sites than at the Zn sites. Specifically, the results of O K-edge scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) and the corresponding X-ray-absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy demonstrated that the impurity (non-stoichiometric) region in ZnO NCs contains a greater defect population than the thick region. The intensity of O K-edge STXM-XANES in the impurity region is more predominant in ZnO NCs than in NWs. The increase in the unoccupied (occupied) density of states at/above (at/below) the conduction-band minimum (valence-band maximum) or the Fermi level is related to the population of defects at the O sites, as revealed by comparing the ZnO NCs to the NWs. The results of O K-edge and Zn L3,2-edge X-ray magnetic circular dichroism demonstrated that the origin of magnetization is attributable to the O 2p orbitals rather than the Zn d orbitals. Further, the local density approximation (LDA) + U verified that vacancies in the form of dangling or unpaired 2p states (due to Zn vacancies) induced a significant local spin moment in the nearest-neighboring O atoms to the defect center, which was determined from the uneven local spin density by analyzing the partial density of states of O 2p in ZnO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...