Highly efficient and low voltage silver nanowire-based OLEDs employing a n-type hole injection layer†
Abstract
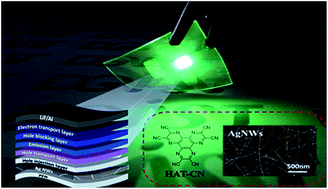
Highly flexible and efficient silver nanowire-based organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have been successfully fabricated by employing a n-type hole injection layer (HIL). The silver nanowire-based OLEDs without light outcoupling structures exhibited excellent device characteristics such as extremely low turn-on voltage (3.6 V) and high current and power efficiencies (44.5 cd A−1 and 35.8 lm W−1). In addition, flexible OLEDs with the silver nanowire transparent conducting electrode (TCE) and n-type HIL fabricated on plastic substrates showed remarkable mechanical flexibility as well as device performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...