Facile fabrication of a near-infrared responsive nanocarrier for spatiotemporally controlled chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy†
Abstract
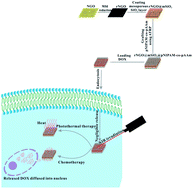
Remote-controlled nanocarriers for drug delivery are of great promise to provide timely, sensitive and spatiotemporally selective treatments for cancer therapy. Due to convenient and precise manipulation, deep penetration through tissues and excellent biocompatibility, near-infrared (NIR) irradiation is a preferred external stimulus for triggering the release of loaded drugs. In this work, for spatiotemporally controlled chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy, a NIR responsive nanocarrier was fabricated using reduced graphene oxide nanosheets (rNGO) decorated with mesoporous silica shell and the subsequent functionalization of the thermoresponsive polymer brushes (pNIPAM-co-pAAm) at the outlet of the silica pore channels. rNGO, which combined with the mesoporous silica shell provide a high loading capacity for anticancer drugs (doxorubicin, DOX), was assigned to sense NIR irradiation for the manipulation of pNIPAM-co-pAAm valve to control the diffusion of loaded DOX. Under NIR irradiation, rNGO would generate heat, which could not only elevate the surrounding temperature over the low critical solution temperature (LCST) of pNIPAM-co-pAAm to open the thermoresponsive polymer valve and promote the diffusion of DOX, but also kill the cancer cells through the hypothermia effect. By manipulating NIR irradiation, the nanocarrier exhibited efficiently controlled release of loaded DOX both in the buffer and in living HeLa cells (the model cancer cells), providing powerful and site-targeted treatments, which can be attributed to synergistic effects of chemo-photothermal therapy. To sum up, this novel nanocarrier is an excellent drug delivery platform in remote-controlled chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy via NIR irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...