Photovoltaic enhancement due to surface-plasmon assisted visible-light absorption at the inartificial surface of lead zirconate–titanate film†
Abstract
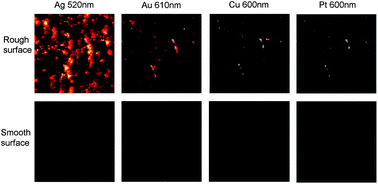
PZT film of 300 nm thickness was deposited on tin indium oxide (ITO) coated quartz by a sol–gel method. Four metal electrodes, such as Pt, Au, Cu and Ag, were used as top electrodes deposited on the same PZT film by sputtering at room temperature. In ITO–PZT–Ag and ITO–PZT–Au structures, the visible light (400–700 nm) can be absorbed partially by a PZT film, and the maximum efficiency of photoelectric conversion of the ITO–PZT–Ag structure was enhanced to 0.42% (100 mW cm−2, AM 1.5G), which is about 15 times higher than that of the ITO–PZT–Pt structure. Numerical simulations show that the natural random roughness of polycrystalline-PZT–metal interface can offer a possibility of coupling between the incident photons and SPs at the metal surface. The coincidence between the calculated SP properties and the measured EQE spectra reveals the SP origin of the photovoltaic enhancement in these ITO–PZT–metal structures, and the improved photocurrent output is caused by the enhanced optical absorption in the PZT region near the metal surface, rather than by the direct charge–transfer process between two materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...