Growth of rutile TiO2 on the convex surface of nanocylinders: from nanoneedles to nanorods and their electrochemical properties†
Abstract
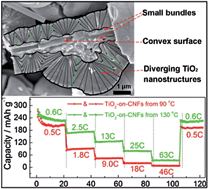
In this work, bundles of rutile TiO2 nanoneedles/nanorods are hydrothermally grown on carbon nanofibers (CNFs), forming free-standing mats consisting of three dimensional hierarchical nanostructures (TiO2-on-CNFs). Morphologies and structures of the TiO2-on-CNFs are studied using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA). Their electrochemical properties as electrodes in lithium ion batteries (LIBs) are investigated and correlated with the morphologies and structures. It is shown that the lateral size of the TiO2 nanoneedles/nanorods ranges from a few nanometers to tens of nanometers, and increases with the hydrothermal temperature. Small interspaces are observed between individual nanoneedles/nanorods, which are due to the diverging arrangement of nanoneedles/nanorods induced by growing on the convex surface of nanocylinders. It is found that the growth process can be divided into two stages: initial growth on the CNF surface and further growth upon re-nucleation on the TiO2 bundles formed in the initial growth stage. In order to achieve good electrochemical performance in LIBs, the size of the TiO2 nanostructures needs to be small enough to ensure complete alloying and fast charge transport, while the further growth stage has to be avoided to realize direct attachment of TiO2 nanostructures on the CNFs, facilitating electron transport. The sample obtained after hydrothermal treatment at 130 °C for 2 h (TiO2-130-2) shows the above features and hence exhibits the best cyclability and rate capacity among all samples; the cyclability and rate capacity of TiO2-130-2 are also superior to those of other rutile TiO2-based LIB electrodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...