Substrate-induced effects on the optical properties of individual ZnO nanorods with different diameters†
Abstract
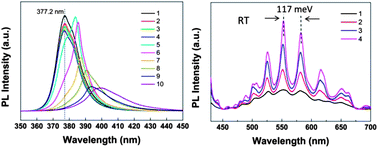
We present the influence of a substrate on the properties of well-dispersed individual ZnO nanorods (NRs) with different diameters, especially on the photoluminescence (PL) properties. The studied ZnO NRs were partially supported by the quartz substrate and partially suspended in air. Continuous redshift and intensity decrease of the near band-edge emission (NBE) were observed along the suspended segment of the ZnO NRs due to the increasing temperature under UV laser excitation, suggesting that the presence of the substrate can effectively enhance the heat-sinking capability of ZnO NRs. Based on the PL measurements on individual suspended ZnO NRs with diameters from 86 nm to 2.35 μm, the redshift of NBE along the suspended segment was more obvious for ZnO NRs with a smaller diameter, indicating that the thermal conductive ability increases as diameter increases. Additionally, by combining the experimental and simulation results, we found that the presence of the substrate also quenched the whispering gallery modes (WGMs) of the ZnO NRs with a diameter above about 350 nm due to the symmetry breaking induced by the quartz substrate which has a larger refractive index compared with air. Our studies confirm that the substrate significantly influences the properties of ZnO NRs. To fully utilize the potential properties of nanomaterials for applications in nanodevices, the substrate-induced effects should be considered thoughtfully.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...