The effect of aryl hydrazono ester containing dipeptides (AHEDs) on mosquito egg-laying behaviour†
Abstract
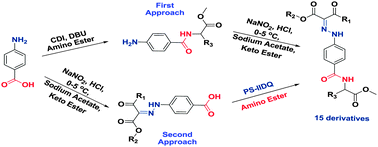
A series of novel aryl hydrazono ester containing dipeptides (AHEDs) were synthesized by using polystyrene-supported 2-isobutoxy-1-isobutoxycarbonyl-1,2-dihydro-quinoline (PS-IIDQ) to study the oviposition responses in Aedes albopictus mosquitoes at 1 ppm and 10 ppm concentrations. Two different synthetic routes have been optimized successfully for the synthesis of target compounds. The pheromone and semiochemical mediated oviposition activity of mosquitoes is a well-known aspect in mosquito behavioral ecology. Structural elucidation of synthesized AHED was achieved by spectral analysis. In a dual choice experiment, the oviposition responses of gravid A. albopictus were evaluated against AHED-1 to AHED-15 at two different concentrations. Among all the compounds, AHED-6 showed the maximum oviposition attractant activity with an oviposition activity index (OAI) of +0.538 at 10 ppm. In contrast to this, AHED-13 exhibited the highest oviposition deterrent activity with an OAI of −0.774 at 1 ppm.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...