Interaction of the NAMI-A complex with nitric oxide under physiological conditions†
Abstract
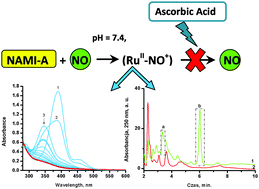
The interference of NAMI-A ([ImH][RuCl4(Im)(DMSO)], Im – imidazole, DMSO – dimethyl sulfoxide) with the metabolism of nitric oxide (NO) has been proposed as one of the possible pathways of the antimetastatic activity of this complex. With regard to this observation we present herein detailed spectrophotometric studies on interaction of the NAMI-A complex with NO. The reactivity of NAMI-A toward NO has been studied in aqueous solution under physiological-like conditions (pH = 7.4, [NaCl] = 0.1 M, T = 37 °C). The ability of NAMI-A as well as its hydrolytic products to bind NO has been confirmed spectrophotometrically and separation of reaction products was performed with application of the HPLC technique. The relatively slow NO binding requires opening up a coordination site in the parent NAMI-A complex via simultaneously occurring hydrolysis. The studies in the presence of albumin showed that NO can coordinate to NAMI-A–albumin adducts. The capability of nitrosyl derivatives (Ru2+–NO+) to undergo reduction of the NO+ moiety in the presence of ascorbic acid, glutathione and dithionite has been studied with application of the NO sensor. The obtained results showed that under selected conditions, nitrosyl complexes cannot liberate nitric oxide via one electron reduction using applied reductants. This is due to the relatively low reduction potential of the NO+ group bound to Ru(II) (−0.69 V), determined in electrochemical studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...