Highly specific and sensitive detection of bisphenol A in water samples using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay employing a novel synthetic antigen
Abstract
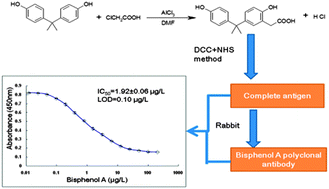
Bisphenol A is a newly discovered endocrine disrupting chemical found in the environment that has estrogenic properties. With the extensive use of plastic products, the diffusion of bisphenol A from these products has caused serious environmental contamination. The present study investigated the synthesis of bisphenol-A antigen and polyclonal antibodies in order to develop a rapid method for the detection of bisphenol A in water. A carboxyl group was introduced into bisphenol A to create a novel hapten capable of coupling with proteins. A rabbit polyclonal antibody with good specificity was prepared by using the novel synthetic antigen. The obtained antibody had a low cross-reaction with other steroid substances. The half inhibitory concentration of the established method was 1.92 ± 0.06 μg L−1, with the lowest limit of detection being 0.10 μg L−1 and the coefficient of variation being less than 10%. The standard recovery rate of water samples was 95.5–105.0%. The method established in this study is an easy, rapid and specific method used for the quantitative detection of bisphenol A in water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...