Morphological analysis of the pancreas and liver in diabetic KK-Ay mice treated with zinc and oxovanadium complexes
Abstract
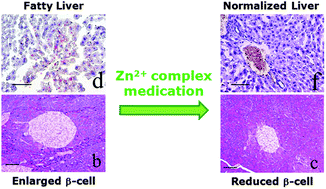
The relationship between biometals, such as zinc (Zn2+), vanadium, copper, cobalt, and magnesium ions, and diabetes therapy has been recognized for several years. In particular, the antidiabetic activities of Zn2+ and oxovanadium (VO2+) complexes have been measured using biochemical approaches. In the present study, diabetic KK-Ay mice were treated with bis(1-oxy-2-pyridine-thiolato)Zn2+ (Zn(opt)2) and bis(1-oxy-2-pyridine-thiolato)VO2+ (VO(opt)2) for 4 weeks, and the antidiabetic activities of these metal complexes were evaluated using biochemical and morphological methods. Additionally, zinc gluconate (Zn(glc)2) and bis(ethylmaltolato)VO2+ (VO(emal)2) were used as reference compounds. Pancreatic islet cells were smaller, and there was a tendency towards a lower islet cell area ratio in Zn(opt)2-treated mice compared with nontreated KK-Ay mice. Furthermore, plasma insulin concentrations were significantly reduced to 27.2% of insulin concentrations in nontreated KK-Ay mice. These results suggest that Zn(opt)2 administration provides morphological and biochemical improvements in hyperinsulinaemia. In contrast, in mice that received Zn(glc)2 and VO2+ complexes, the islet cell size and islet cell area ratio did not differ from those in nontreated controls. Zn(opt)2- and VO(opt)2-treated mice exhibited significantly lower fat deposition and fat deposition area ratio in the liver (63.6% and 65.8% of nontreated KK-Ay mice, respectively) compared to those observed in nontreated KK-Ay mice. The differences in morphological improvements of the pancreas and liver owing to Zn(opt)2 or VO(opt)2 treatment may be explained by differences in the sites of actions of Zn2+ and VO2+ complexes in different organs in KK-Ay mice. In conclusion, Zn(opt)2 exhibited superior antidiabetic effects over those of VO(opt)2, and this was owing to greater amelioration of the morphological parameters of the liver and pancreas.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...