Metallomics of two microorganisms relevant to heavy metal bioremediation reveal fundamental differences in metal assimilation and utilization
Abstract
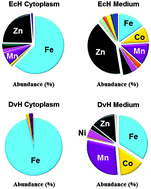
Although as many as half of all proteins are thought to require a metal cofactor, the metalloproteomes of microorganisms remain relatively unexplored. Microorganisms from different environments are likely to vary greatly in the metals that they assimilate, not just among the metals with well-characterized roles but also those lacking any known function. Herein we investigated the metal utilization of two microorganisms that were isolated from very similar environments and are of interest because of potential roles in the immobilization of heavy metals, such as uranium and chromium. The metals assimilated and their concentrations in the cytoplasm of Desulfovibrio vulgaris strain Hildenborough (DvH) and Enterobacter cloacae strain Hanford (EcH) varied dramatically, with a larger number of metals present in Enterobacter. For example, a total of 9 and 19 metals were assimilated into their cytoplasmic fractions, respectively, and DvH did not assimilate significant amounts of zinc or copper whereas EcH assimilated both. However, bioinformatic analysis of their genome sequences revealed a comparable number of predicted metalloproteins, 813 in DvH and 953 in EcH. These allowed some rationalization of the types of metal assimilated in some cases (Fe, Cu, Mo, W, V) but not in others (Zn, Nd, Ce, Pr, Dy, Hf and Th). It was also shown that U binds an unknown soluble protein in EcH but this incorporation was the result of extracellular U binding to cytoplasmic components after cell lysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...