Sulfonium ions as inhibitors of the mycobacterial galactofuranosyltransferase GlfT2†
Abstract
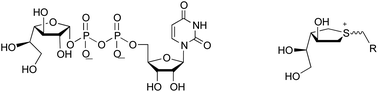
The mycobacterial cell wall possesses a core galactan moiety composed of approximately 30 galactofuranosyl residues attached via alternating β-(1→5) and β-(1→6) linkages. A bifunctional galactofuranosyltransferase, GlfT2, is one of two essential enzymes for mycobacterial cell wall biosynthesis. The enzymatic reactions catalyzed by GlfT2 undoubtedly proceed by way of a transition state that has significant oxocarbenium-ion character. In this paper, a series of sulfonium ion compounds were designed and synthesized as analogues of the donor substrate, uridine diphosphate-galactofuranose, as potential inhibitors of GlfT2. The compounds contain moieties that mimic both galactofuranose and uridine diphosphate domains, and carry a permanent positive charge to mimic the oxocarbenium ion-like transition state. These compounds were evaluated against Glf2 using a coupled spectrophotometric assay, and some were shown to be weak inhibitors of the enzyme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...