Improved synthesis of 4-/6-substituted 2-carboxy-1H-indole-3-propionic acid derivatives and structure–activity relationships as GPR17 agonists†
Abstract
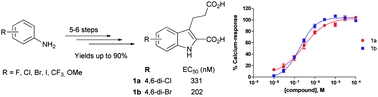
The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR17 was shown to be involved in myelin repair and has been proposed as a novel drug target for the treatment of brain and spinal cord injury and for multiple sclerosis. Recently, 3-(2-carboxy-4,6-dichloro-indol-3-yl)propionic acid (MDL29,951, 1a) was discovered and characterized as a potent synthetic GPR17 agonist. In the present study we substantially optimized the preparation of 1a, which is carried out via Japp–Klingemann condensation of 3,5-dichlorophenyldiazonium chloride and deprotonated 2-(ethoxycarbonyl)cyclopentanone yielding phenylhydrazone derivative 5a followed by Fischer indole (diaza-Cope) rearrangement. A robust synthesis of 1a (75% yield) was developed to allow upscaling of the procedure. The developed method was applied to the synthesis of a series of 10 derivatives, eight of which represent new compounds. Biological evaluation in calcium mobilization assays using 1321N1-astrocytoma cells recombinantly expressing the human GPR17 provided first insights into their structure–activity relationships. 3-(2-Carboxy-4,6-dibromo-indol-3-yl)propionic acid (1b) showed similar potency to 1a and represents the most potent synthetic GPR17 agonist described to date with an EC50 value of 202 nM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...