Gene module based regulator inference identifying miR-139 as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer†
Abstract
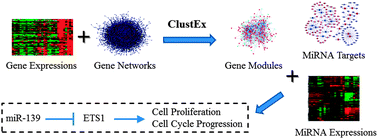
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancer types worldwide. Identification of the key regulators of the altered biological networks is crucial for understanding the complex molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer. We proposed a gene module based approach to infer key miRNAs regulating the major gene network alterations in cancer tissues. By integrating gene differential expression and co-expression information with a protein–protein interaction network, the differential gene expression modules, which captured the major gene network changes, were identified for colorectal cancer. Then, several key miRNAs, which extensively regulate the gene modules, were inferred by analyzing their target gene enrichment in the modules. Among the inferred candidates, three miRNAs, miR-101, miR-124 and miR-139, are frequently down-regulated in colorectal cancers. The following computational and experimental analyses demonstrate that miR-139 can inhibit cell proliferation and cell cycle G1/S transition. A known oncogene ETS1, a key transcription factor in the gene module, was experimentally verified as a novel target of miR-139. miR-139 was found to be significantly down-regulated in early pathological cancer stages and its expression remained at very low levels in advanced stages. These results indicate that miR-139, inferred by the gene module based approach, should be a key tumor suppressor in early cancer development.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...