2,4-Dihydroxypyrimidine is a potential urinary metabolite biomarker for diagnosing bipolar disorder†
Abstract
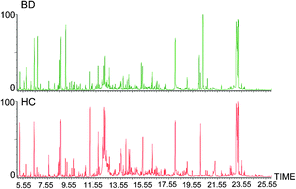
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a common and debilitating mental disorder. However, there are no biomarkers available to aid in the diagnosis of this disorder. Here, we used a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) based metabonomic method to characterize the urinary metabolic profiling of BD subjects and healthy controls to identify and validate urinary metabolite biomarkers for BD. Multivariate statistical analysis was used to visualize group discrimination and identify differentially expressed urinary metabolites in BD subjects relative to the healthy controls. Multivariate statistical analysis showed that the BD group was significantly distinguishable from the healthy control. Totally, 37 urinary metabolites responsible for discriminating BD subjects from healthy controls were identified. Interestingly, of 37 differential metabolites, 2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine was identified as an effective diagnostic biomarker for BD, yielding an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.889 in the training samples (45 BD subjects and 61 healthy controls) and 0.805 in the test samples (26 BD subjects and 33 healthy controls). Our findings suggest that 2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine is a promising candidate urinary biomarker for BD, which may facilitate development of a urine-based diagnostic test for BD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...