High-content screening of yeast mutant libraries by shotgun lipidomics†
Abstract
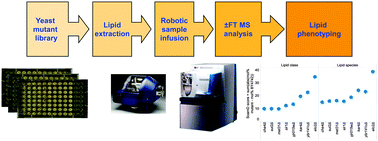
To identify proteins with a functional role in lipid metabolism and homeostasis we designed a high-throughput platform for high-content lipidomic screening of yeast mutant libraries. To this end, we combined culturing and lipid extraction in 96-well format, automated direct infusion nanoelectrospray ionization, high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry, and a dedicated data processing framework to support lipid phenotyping across hundreds of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants. Our novel approach revealed that the absence of genes with unknown function YBR141C and YJR015W, and the transcription factor KAR4 precipitated distinct lipid metabolic phenotypes. These results demonstrate that the high-throughput shotgun lipidomics platform is a valid and complementary proxy for high-content screening of yeast mutant libraries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...