Assessment of early triage for acute radiation injury in rat model based on urinary amino acid target analysis†
Abstract
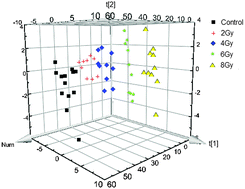
Rapid radiation injury early triage after a radiological or nuclear exposure is vital for treatment of a large number of wounded people. Owing to the high-throughput analysis and minimally invasive nature of sample collection, radiation metabolomics has been recently applied to radiation damage research. In the present study, exploring the feasibility of estimating the acute radiation injury for early triage by means of urinary amino acid target analysis was attempted using a high performance liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS) technique combined with multivariate statistical analysis. The non-linear kernel partial least squares (KPLS) model was used to separate the control and different radiation dose groups. The classification of different groups was performed after feature selection instead of before feature selection, because of its better separation. The classification accuracy at various radiation injury levels at different time points (5, 24, 48 and 72 h) post-irradiation exposure was investigated. For most of the radiation damage levels, the classification accuracy at 72 h after exposure was superior to that at earlier time points. Additionally, the potential radiation injury biomarkers selected suggested that the urea cycle, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, alanine, aspartate and glutamine metabolism and related metabolic pathways were involved. The findings suggest that non-invasive urinary biomarkers have great potential for serving as an effective tool for rapid triage of mass casualties in nuclear accidents and understanding the pathogenesis of radiation injury.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...