Fecal metabonomic study of a polysaccharide, MDG-1 from Ophiopogon japonicus on diabetic mice based on gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC TOF/MS)
Abstract
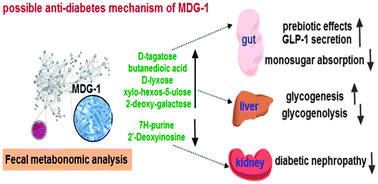
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder with systemic complications and has been a worldwide epidemic. Ophiopogon japonicus is a traditional Chinese medicine used to treat diabetes for thousands of years. From our previous work, we know that MDG-1, a water-soluble β-D-fructan polysaccharide from O. japonicas could treat T2DM experimentally. However, MDG-1 is poorly absorbed and its mechanism of action is still unknown. Therefore, a GC TOF/MS-based metabonomic approach in combination with multivariate statistical analysis was performed to investigate the mechanism of MDG-1 in a spontaneous diabetic model. Female diabetic KKay mice (21 weeks old) were randomly divided into a diabetic group (n = 6, gavaged with distilled water) and a MDG-1-Diabetic group (n = 7, gavaged with MDG-1, 300 mg kg−1) and female C57BL/6 mice (21 weeks old) were set as controls (n = 6, gavaged with distilled water). After 8-weeks of treatment, feces samples were collected for GC-TOF/MS analysis. Consequently, 12 potential biomarkers were identified, including monosugars (D-tagatose, D-lyxose, D-erythrose, xylo-hexos-5-ulose, 2-deoxy-galactose), butanedioic acid, amino acids (phenylalanine, L-lysine, L-methionine, L-aspartic acid) and purine derivatives (7H-purine, 2′-deoxyinosine). We assume the monosugars and butanedioic acid were the fermentation products of MDG-1 by intestinal microbes and MDG-1 actions against diabetes might be accomplished through the absorbable monosugars and butanedioic acid via suppressing intestinal glucose absorption, enhancing liver glycogenesis, inhibiting glycogenolysis and promoting GLP-1 secretion. Besides, MDG-1 might alleviate diabetes and diabetic nephropathy by reducing 7H-purine and 2′-deoxyinosine. Further omics-driven studies including genomics, proteomics and metabonomics were considered to be carried out to provide direct evidence of gut microbiome contribution to MDG-1 actions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...