Binding of ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol to bovine serum albumin: a comparative study
Abstract
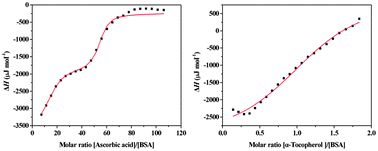
Binding of ascorbic acid (water-soluble antioxidant) and α-tocopherol (lipid-soluble antioxidant) to bovine serum albumin (BSA) has been studied using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), in combination with fluorescence spectroscopy, UV-vis absorption spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Thermodynamic investigations reveal that ascorbic acid/α-tocopherol binding to BSA is driven by favorable enthalpy and unfavorable entropy, and the major driving forces are hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces. For ascorbic acid, the interaction is characterized by a high number of binding sites, which suggests that binding occurs by a surface adsorption mechanism that leads to coating of the protein surface. For α-tocopherol, one molecule of α-tocopherol combines with one molecule of BSA and no more α-tocopherol binding to BSA occurs at concentration ranges used in this study. Fluorescence experiments suggest that ascorbic acid has predominantly a “sphere of action” quenching mechanism, whereas, for α-tocopherol, the quenching mechanism is “static quenching” and due to the formation of a ground state complex. Additionally, as shown by the UV-vis absorption, synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy, and FT-IR, ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol may induce conformational and microenvironmental changes of BSA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...