Optically induced dielectropheresis sorting with automated medium exchange in an integrated optofluidic device resulting in higher cell viability†
Abstract
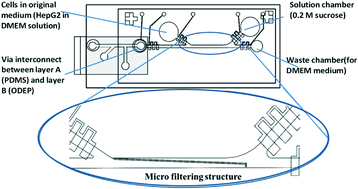
We demonstrated the integration of a microfluidic device with an optically induced dielectrophoresis (ODEP) device such that the critical medium replacement process was performed automatically and the cells could be subsequently manipulated by using digitally projected optical images. ODEP has been demonstrated to generate sufficient forces for manipulating particles/cells by projecting a light pattern onto photoconductive materials which creates virtual electrodes. The production of the ODEP force usually requires a medium that has a suitable electrical conductivity and an appropriate dielectric constant. Therefore, a 0.2 M sucrose solution is commonly used. However, this requires a complicated medium replacement process before one is able to manipulate cells. Furthermore, the 0.2 M sucrose solution is not suitable for the long-term viability of cells. In comparison to conventional manual processes, our automated medium replacement process only took 25 minutes. Experimental data showed that there was up to a 96.2% recovery rate for the manipulated cells. More importantly, the survival rate of the cells was greatly enhanced due to this faster automated process. This newly developed microfluidic chip provided a promising platform for the rapid replacement of the cell medium and this was also the first time that an ODEP device was integrated with other active flow control components in a microfluidic device. By improving cell viability after cell manipulation, this design may contribute to the practical integration of ODEP modules into other lab-on-a-chip devices and biomedical applications in the future.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...