Double-pulse LIBS combining short and long nanosecond pulses in the microjoule range
Abstract
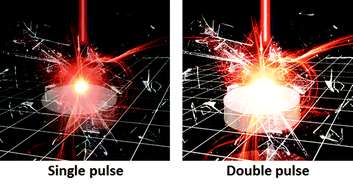
The present study investigates the collinear double-pulse LIBS (DP-LIBS) configuration using microjoule nanosecond pulses. It is shown that this approach can achieve typical double pulse improvement in the analytical performances for elemental analysis of aluminium alloys. In addition, the effect of the chronological sequence of the short and long nanosecond pulses in the collinear DP-LIBS experiment was also studied. The results show a significant increase of the intensity and repeatability of the emission signals in the double pulse configuration. Standard DP-LIBS signal improvement over the signal-to-noise ratio and the signal-to-background ratio for the analytical lines of different elements has been observed in comparison to single pulse LIBS of equal energy. Limits of detection in the low μg g−1 range have been obtained for the different elements studied. The improvement resulting from the use of DP-LIBS was about 2–4 fold when compared to SP-LIBS in all cases. These results are useful in the context of studies investigating how the μLIBS will assist in the development of portable LIBS systems and improve the utility of this spectroscopy technique for field applications. Finally, the plasma temperature is found to be approximately less than 15% higher with the double-pulse.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...