Optimisation of laser parameters for the analysis of sulphur isotopes in sulphide minerals by laser ablation ICP-MS†
Abstract
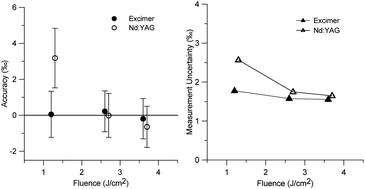
The effects of laser type (Nd:YAG and excimer lasers) and their analytical parameters on 34S/32S isotopic fractionation during LA-ICP-MS analysis were investigated. Laser fluence has a larger fractionation effect when ablating pyrite with the New Wave Nd:YAG 193 nm laser, compared to the Resonetics 193 nm excimer laser which did not produce significant fractionation over the same range of fluence (1.3–3.7 J cm−2). Matrix effects occurred between pyrite and bornite on both laser systems, especially at low fluence. However, matrix effects can be reduced with increasing fluence lessening the need for matrix matched reference materials. The effects of interface tubing configuration were also investigated and the addition of a ‘squid’ mixing device, a coil of small diameter Tygon tubing and a small volume glass bulb, was found to improve signal precision and reproducibility and decrease the washout time of the S signal between analyses. The degassing of air from the inner surfaces of the interface tubing can produce significant isotopic drift (8‰ h−1), hence flushing the tubing prior to analyses is crucial for reproducible analyses. The isotopic composition and homogeneity of a range of sulphide minerals were characterised for use as potential reference materials. We present preliminary data for a large, isotopically homogeneous pyrite crystal (PPP-1) which could be considered as a new isotopic reference material (δ34SV-CDT = 5.3 ± 0.2‰).
- This article is part of the themed collection: Geological applications of laser ablation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...