Collection of atmospheric gaseous mercury for stable isotope analysis using iodine- and chlorine-impregnated activated carbon traps
Abstract
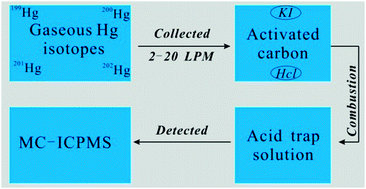
The trace levels of Hg in the atmosphere pose an analytical challenge for Hg stable isotope research. Here we propose a new method using iodine- and chlorine-impregnated activated carbon (IC and CLC) traps for collection of atmospheric total gaseous mercury (TGM). Decontamination of IC and CLC yielded low blank levels of 0.3 ng Hg per g of carbon, corresponding to <3% of collected Hg. IC and CLC traps with 250, 600 and 1000 mg of a sorbent collected TGM efficiently (>92%) at flow rates of 2, 10, and 20 LPM respectively. These flow rates enabled high-resolution (12–24 h) and low-resolution (bi-weekly) sampling of TGM. We also tested bi-weekly TGM sampling using commercial gold traps at a low flow rate of 0.3 LPM. TGM collected on IC and CLC traps at the Pic du Midi Observatory was desorbed and pre-concentrated into aqueous solution using an off-line combustion and trapping technique. Hg isotopic compositions were determined using cold vapor multicollector-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (CV-MC-ICPMS). The field measurements showed mean recoveries of 88 ± 5% (1σ, n = 11) for 12 h and 24 h and 90 ± 6% (1σ, n = 25) for the bi-weekly field samples. Laboratory additions of Hg vapor of known isotopic composition to CLC and gold traps indicated that recoveries >81% did not induce isotopic artifacts. Samples with recoveries <81% showed a positive mass dependent fractionation bias. Typical expanded uncertainties (2σ) on δ202Hg (mass dependent fractionation of 202Hg) and Δ199Hg (mass independent fractionation of 199Hg) for the bi-weekly sampling, processing and CV-MC-ICPMS analysis are 0.13‰ and 0.09‰, respectively. Our study suggests that the proposed method meets the criteria for accurate and precise measurements of atmospheric TGM isotopic compositions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...