Original polyols based on organosolv lignin and fatty acids: new bio-based building blocks for segmented polyurethane synthesis†
Abstract
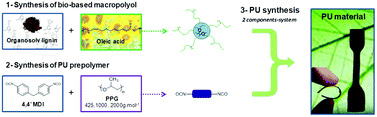
A macropolyol was successfully prepared by combining two different biomolecules from biomass, i.e. lignin and oleic acid, using a solvent-free and catalyst-free method. The chemical structures of this original lignin–fatty acid based polyol and its intermediates were determined by 1H NMR and FT-IR analyses. A series of polyurethanes (PUs) were then prepared by a two-step procedure. Three linear isocyanate prepolymers were first synthesized from 4,4′-methylenebis(phenyl isocyanate) and poly(propylene)glycol of different molecular weights (PPG – 425, 1000 and 2000 g mol−1). These intermediates were used to obtain different PU macromolecular architectures by varying reaction parameters in the presence of the lignin–fatty acid based macropolyol. The final lignin-based polyurethanes were thoroughly chemically characterized by FT-IR studies, whereas the properties of these polymers were assessed by DSC, TGA, DMTA, and tensile test experiments. All these were performed in order to evaluate the influence of the NCO : OH molar ratio (from 0.2 to 1.0) as well as the influence of the PPG chain length. These new polymers with controlled architectures presented advanced properties. Their high biobased content (until 89%) depicts an important output for the valorisation of lignin and they may be an optimal alternative to conventional PUs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...