Installation of protected ammonia equivalents onto aromatic & heteroaromatic rings in water enabled by micellar catalysis†
Abstract
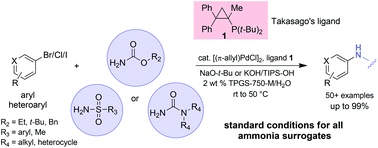
A single set of conditions consisting of a palladium catalyst, a commercially available ligand, and a base, allow for several types of C–N bond constructions to be conducted in water with the aid of a commercially available “designer” surfactant (TPGS-750-M). Products containing a protected NH2 group in the form of a carbamate, sulfonamide, or urea can be fashioned starting with aryl or heteroaryl bromides, iodides, and in some cases, chlorides, as substrates. Reaction temperatures are in the range of room temperature to, at most, 50 °C, and result in essentially full conversion and good isolated yields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...