Chemical recycling of the waste anodic electrolyte from the TiO2 nanotube preparation process to synthesize facet-controlled TiO2 single crystals as an efficient photocatalyst†
Abstract
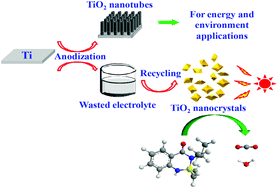
Anodization has been reported to be an effective electrochemical method to prepare vertically ordered, upright oriented TiO2 nanotubes for efficient photocatalysis, solar cells and many other fields. However, this process generates a large amount of residual anodic electrolytes that are rich in toxic fluorides, which are usually discarded and cause environmental contamination. Here, we propose a facile and effective method to prepare both pristine and N-doped TiO2 nanocrystals based on the recycling of waste ethylene glycol electrolyte from the widely-used anodic process. Under identical conditions, both the pristine and N-doped TiO2 nanocrystals exhibited nearly twice as high photocatalytic activity in decomposition of humic acids and bentazone than Degussa P25, one of the best commercial TiO2 photocatalysts. The preparation method had obvious economic and environmental benefits. The prepared TiO2 nanocrystals possessed superior photocatalytic degradation capacities for refractory pollutants, and could be used for efficient water treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...