Polyphenol-rich apple (Malus domestica L.) peel extract attenuates arsenic trioxide induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells via its antioxidant activity†
Abstract
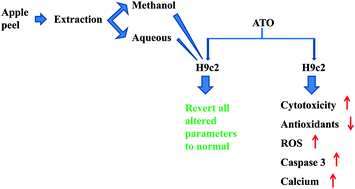
Evidences suggest that apple peel has a wide range of polyphenols having antioxidant activity and its consumption has been linked with improved health benefits. Arsenic trioxide (ATO) is a very effective drug for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) but it leads to cardiotoxicity mediated through alterations in various cardiac ion channels and by increasing the intracellular calcium level and reactive oxygen species (ROS). The aim of the present investigation was to study the effect of methanolic extract of apple peel (APME) and aqueous extract of apple peel (APAE) on ATO (5 μM) induced toxicity in the H9c2 cardiac myoblast cell line. We estimated the cellular status of innate antioxidant enzymes, level of ROS, mitochondrial superoxide, glutathione and intracellular calcium with ATO and apple peel extracts. Prior to the cell line based study, we had evaluated the antioxidant potential of apple peel extract by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), total reducing power (TRP), superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, in addition to quantifying total phenolic and flavonoid content. Both the extracts showed considerable antioxidant activity in cell-free chemical assays. In addition, both APME and APAE prevented the alteration in antioxidant status induced by ATO in H9c2 cells. Significant differential alterations had been observed in the activity of lactate dehydrogenase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, thioredoxin reductase, xanthine oxidase, calcium overload and caspase 3 activity with ATO. The overall result revealed the protective property of polyphenol-rich apple peel extract against ATO induced cardiac toxicity via its antioxidant activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...